History - Greece
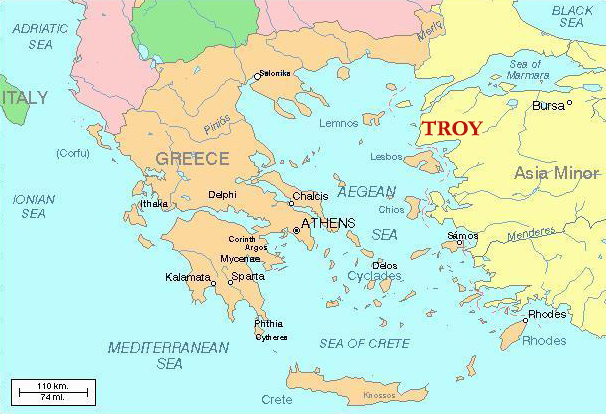
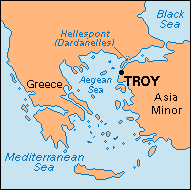
Troy was an ancient city in Asia Minor (now part of Turkey). Ruins of Troy have yielded historical relics that are about 5,000 years old. It was the dominant culture in the Western world when the Greek civilization began its ascent.
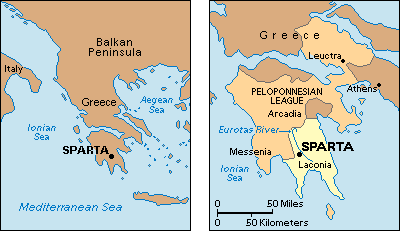
Sparta was the most powerful city-state of ancient Greece, and the capital of Laconia. By 500 B.C., Sparta had forced nearby city-states to enter the Peloponnesian League. The map on the left shows the location of Sparta in ancient Greece. The detailed map on the right shows Sparta and the Peloponnesian League.
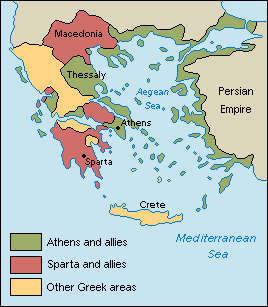
Athens and Sparta organized rival alliances in the fourth century BCE. The Delian Leaague included Athens and other city-states on the Aegean coast and on islands in the Aegean Sea. The Peloponnesian League, led by Sparta, included most of the Peloponnesus peninsula and Macedonia. The rivalry between the two city-states erupted in the Peloponnesian War, which Sparta won.
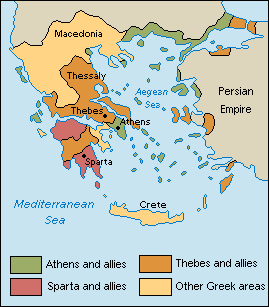
Fighting among Greek city-states continued after the Peloponnesian War (431-404 BCE). The three biggest city-states were Athens, Sparta, and Thebes. Athens and its allies extended along the Aegean coast and to some Aegean islands. Sparta and its allies lay in the northern and southern areas of the Peloponnesus peninsula. Lands allied with Thebes covered most of present-day Greece, part of the Peloponnesus peninsula, and some coastal areas of Asia Minor. Macedonia and the island of Crete contained smaller city-states. Sparta's domination ended in 371 BCE, after which time Thebes briefly held power.
| Roman Republic 510 BCE - 40 BCE | |
| Roman Empire 20 CE - 360 CE | |
| Eastern Roman Empire 405 CE - 1453 CE | |
| Western Roman Empire 405 CE - 480 CE |
History - Rome
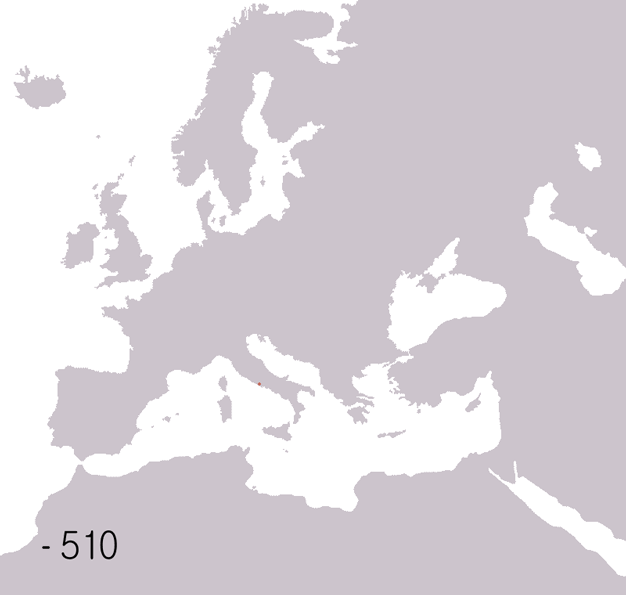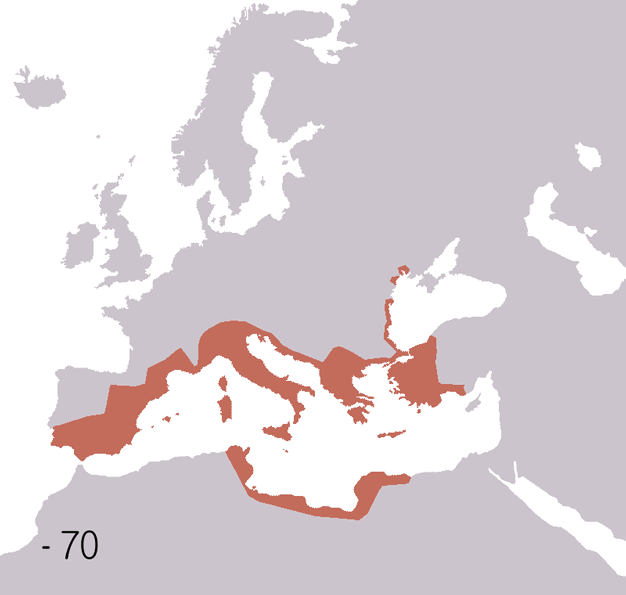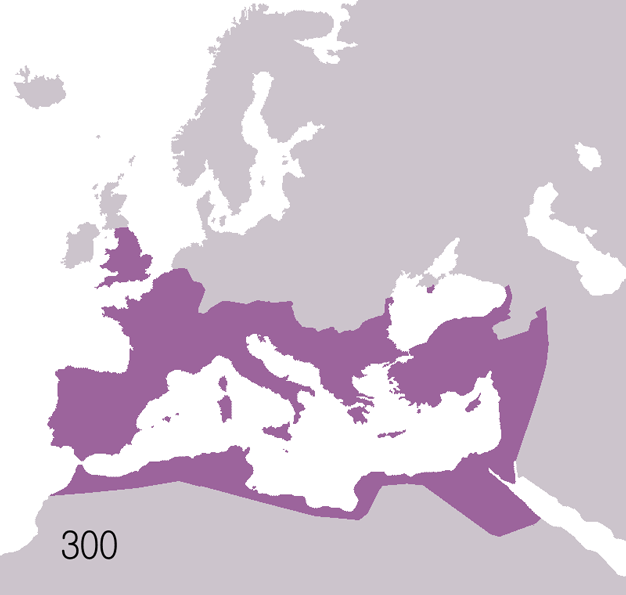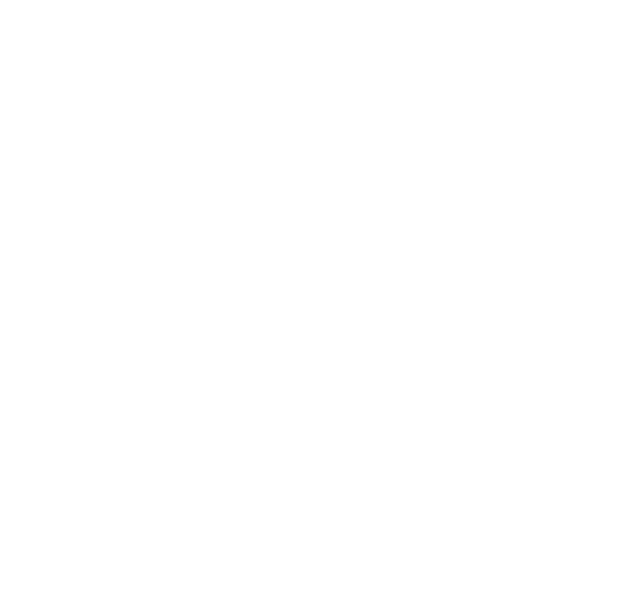
Animated map of the Roman Republic and Empire.
Years shown: 510 BCE, 320 BCE, 300 BCE, 270 BCE, 220 BCE, 190 BCE, 140 BCE, 70 BCE, 40 BCE, 20 CE, 70 CE, 140 CE, 230 CE, 300 CE, 360 CE, 405 CE, 420 CE, 450 CE, 480 CE, 530 CE.