Introduction to Modernism

In the mid-1800s, people began to lose faith in those political, social, economic, and religious institutions that proclaimed that they had "the truth." But people saw that "truth" wasn't objective; it depended on your point of view. In Modernist texts, there is a movement away from the apparent objectivity provided by omniscient third-person narrators, fixed narrative points of view, and clear-cut moral positions. Faulkner's multiply-narrated stories are an example of this aspect of Modernism. Just as in other aspects of life, first-person narrators might not be trustworthy. They may not know what is going on, or they may be trying to deliberately hide what they know. Readers, then, have to pay close attention, because Modernist texts sometimes have gaps in them that must be explored. |

Narrators don't always tell the truth, even when they know it. |
The modern world, and Modernist ideas, couldn't be neatly categorized through the intellectual constructs that worked so well in the post-Enlightenment world. Because they attempted to reflect the world as they saw it around them, Modernists texts didn't fit neatly into the existing genres or forms that worked so well for centuries. Modernist writers blurred the received distinctions between literary genres; their poetry might seem more documentary (as in T.S. Eliot or ee cummings), and their prose might read like poetry (as in Virginia Woolf or James Joyce). Because they focused on subjective expression, Modernist texts could be an amalgam of styles and modes. Joyce's Ulysses is a monumental example of this. In her Tender Buttons, Gertrude Stein sought to "create a word relationship between the word and the things seen." The resulting text can be considered prose, poetry, both, or something else, perhaps, "cubist writing" or "abstract proems."
|

Mixing old & new styles & forms, so it's more difficult to get a handle on the genre of a work. |
Modernism places an emphasis on fragmented forms, discontinuous narratives, and random-seeming collages of different materials. Narration comes through fragmented, internalized, or multiple perspectives or viewpoints. These gaps and fractures make Modernist texts difficult for readers. Previous writers filled in all the gaps for their readers; readers had all the information they needed to understand a text. But Modernist writers are allusive and intertextual; they hint at other meanings, but leave it to the reader to connect the dots and create meaning.
|
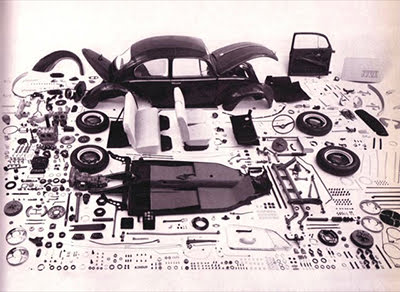
DIY, Dear Reader! It's up to you to put it together. |
Modernist art has a tendency toward reflexivity, or self-consciousness, about the production of the work of art, so that each piece calls attention to its own status as a production, as something constructed and consumed in particular ways. Take a look at this poem by William Carlos Williams, "The Red Wheelbarrow." Once you've read it, answer this question: what is it that depends upon that red wheelbarrow? There's only one thing for certain; the rest are all just flights of our imaginations. The Red Wheelbarrow
|
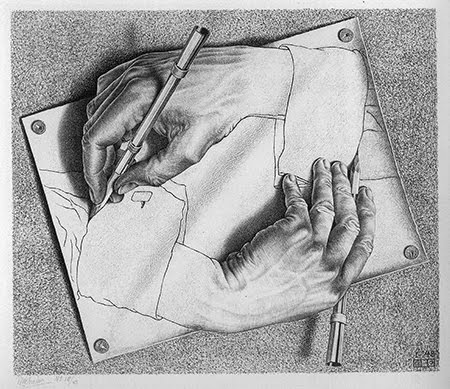
You're looking at a piece of art. |
The heroic individualism of Romanticism gives way to isolation, eccentricity, anti-social behavior, and anti-heroism. Secondary characters are archetypes, or symbolic, or allegorical. Contemporary psychology informs characterization, which leads to complicated, disordered characters. (Freud's id-ego-superego and the unconscious; Jung's archetypes--"the shadow, the wise old man, the child, the mother ... and her counterpart, the maiden, and lastly the anima in man and the animus in woman.") But it's not just an awareness of psychology that makes for complicated characters. Writers only needed to look at the world around them—especially after WWI—to see that aberrations from the norm weren't limited to individuals. Entire societies could be considered through the same lens.
|

They're all the products of a Modernist sensibility |
In Modernism, there's a rejection of the distinction between "high" and "low" or popular culture, both in choice of materials used to produce art and in methods of displaying, distributing, and consuming art. So somone like T.S. Eliot could quote from the Bible in one line, then turn around and allude to a scandalously obscene Australian marching song in the next line, and both lines would make sense.
|

High Culture? Low Culture? It's all fair game. |
One of the central themes of Modernism is alienation, the sense of being separated from society or even from one's own self. It was seen as an unavoidable characteristic of modern life. Increased mechanization alienated all humans from the natural world, while modern workers were removed from the meaning of their work, or any sense of satisfaction with that work. The institutions in which society had placed its trust (national governments, organized religions and individual faith, the workplace, etc.) were all seen to be incapable of addressing or making sense of the modern world. What place did something like noblesse oblige in the face of the horrors of WWI trench warfare? Peoples' understandings of what constituted meaning were shaken by the terror, barbarity, and inhumanity that we saw we were capable of. The ties that used to bind society together were unraveling, leaving us to become isolated. |

How can we be together when we have nothing in common? |
Mary Klages, University of Colorado, Boulder
Craig White, University of Houston - Clear Lake

Some Attributes Of Modernist Literature
The locating of meaning from the viewpoint of the individual; the use of narrators located within the action of the fiction, experiencing from a personal, particular (as opposed to an omniscient, "objective") perspective; the use of many voices, contrasts and contestations of perspective; the consequent disappearance of the omniscient narrator.
An emphasis on the process of perception and knowing: the use of devices (formal, linguistic, representational), to present more closely the texture or process or structure of knowing and perceiving.
The "reality" of realist fiction is replaced by a move toward a presentation of experience as layered, allusive, discontinuous; the use, to these ends, of fragmentation and juxtaposition, motif, symbol, allusion (jump-cuts).
It is not something that, if used correctly, will allow us to "see through" to reality. Rather, language is seen as a complex, nuanced site of our construction of the "real"; language is "thick," with multiple meanings.
Traditional forms cannot capture the modern experience. New forms must be found to present differently, afresh, the structure, the connections, and the experience of life.
This includes trying to capture the "flow" of personal experience, through devices such as stream of consciousness.
Cognitive structures like psychoanalysis, myth, the symbolic apprehension and comprehension of reality, etc., offer a way of understanding more than just fleeting moments of time.
The world is moved "inside," structured symbolically or metaphorically -- as opposed to the Romantic interaction with transcendent forces acting through the exterior world, and Realist representations of the exterior world as a physical, historical, contiguous site of experience. David Lodge suggests in Modes of Modern Writing that the realist mode of fiction is based on metonymy, or contiguity, and the modernist mode is based on metaphor, or substitution.
Time becomes either symbolic or psychological (time as innerly experienced). Time is used as well more complexly as a structuring device through a movement backwards and forwards through time, the juxtaposing of events of different times, and so forth.
As above, this is seen to be more representative of "reality" — as opposed to "closed" endings, in which matters are resolved.
This can result in a symbolic, or ontological, or epistemic ground for reality. We can see it through the device of "epiphany" (Joyce), "inscape" (Hopkins), "moment of being" (Woolf), "Jetztzeit" (Benjamin) — the moment of revelation of a reality beneath and grounding appearances.
Modernism critiques the traditional values of the culture; lays bare the loss of meaning and hope in the modern world, and explores how this loss may be faced.
Lye, John. "Some Attributes of Modernist Literature." ENGL 2F55 Course Notes, Brock University, 2008, brocku.ca/english/courses/2F55/modernism.php.
[This page has been taken down, but is available through the Internet Archive.]

Some Cultural Forces Driving Literary Modernism
Some of the major issues to which 20th-century literature responded in ways generally known as "Modernism" are:
A sense of the loss of "ontological ground"; a loss of confidence that there exists a reliable, knowable ground of value and identity. Contributing factors include:
- the challenges to 19th century science and its confidence in its ability to explain the universe;
- industrialization, and the consequent displacement of persons from their previous physical and psychic groundings; (including a pervasive sense that masculinity and masculine authority had been undermined; that mass culture was a "feminizing" force)
- the association of Christianity with capitalism, and with an oppressive often hypocritical moralism;
- the critical historical study of biblical texts and the consequent challenge to revelation;
- the popularization of evolutionary theory;
- a growing awareness of a variety of cultures which had differing but cogent world-views;
- changes in philosophical thought which suggested that 'reality' was an internal and changeable, not an externally validated, concept.
* Ontology is the study of what "being" is; it is always accompanied by epistemological issues, that is, of questions how we know and what it is to know. Ontological ground is then that which gives us a sense of the surety of being itself.
A sense that our culture has lost its bearings, that there is no center, no cogency, that there is a collapse of values or a bankruptcy (interesting metaphor) of values. As Yeats wrote in "The Second Coming" (1920):
Things fall apart; the centre cannot hold;
Mere anarchy is loosed upon the world.
The blood-dimmed tide is loosed, and everywhere
The ceremony of innocence is drowned;
The best lack all conviction, while the worst
Are full of passionate intensity.
This loss of faith in a moral center and moral direction is based (in part) on the important recognition that the traditional values have, after all, led only to a horrid war, industrial squalor, the breakdown of traditional rural society, exploitation of other cultures and races, and a society built on power and greed. W.W.I was a gruesome wake-up call.
A shift in paradigms from the closed, finite, measurable, cause-and-effect universe of 19th century science to an open, relativistic, changing, strange universe. Einstein was a modernist thinker.
The locus of judgment moves from the traditional sites — consensus, social authority and textual authority — to individual judgment and phenomenological (lived experience) validation, hence to the locating of meaning (and, in a sense, "truth") in individual experience.
The development of studies and ideas which have as their focus the nature and functioning of the individual: the discipline of psychology; a growing democratization in politics; in aesthetics, movements such as impressionism and cubism which focus on the process of perception.
Discovery that the forces governing behavior, and particularly the most powerful and formative ones, are hidden: this in the realms of psychology, economics, politics — Marx, Freud, Nietzsche, etc.
A move to the mystical and the symbolic as ways of recovering a sense of the holy in experience and of recreating a sustainable ontological ground — Yeats and the development of symbolic thought, Jung and the concept of universal archetypes; Lawrence with his notions of the creative mystery and blood knowledge, and so forth.
Lye, John. "Some Cultural Forces Driving Literary Modernism." ENGL 2F55 Course Notes, Brock University, 2009, brocku.ca/english/courses/2F55/forces.php.
[This page has been taken down, but is available through the Internet Archive.]

For much of its history, "modern" has meant something bad. In a general sense it meant having to do with recent times and the present day, but we shall deal with it here in a narrow sense more or less synonymous with that of "modernist." It is not so much a chronological designation as one suggestive of a loosely defined congeries of characteristics. Much twentieth-century literature is not "modern" in the common sense, as much that is contemporary is not. Modern refers to a group of characteristics, and not all of them appear in any one writer who merits the designation modern.
In a broad sense modern is applied to writing marked by a strong conscious break with tradition. It employs a distinctive kind of imagination that insists on having its general frame of reference within itself. It thus practices the solipsism of which Allen Tate accused the modern mind: It believes that we create the world in the act of perceiving it. Modern implies a historical discontinuity, a sense of alienation, loss, and despair. It rejects not only history but also the society of whose fabrication history is a record. It rejects traditional values and assumptions, and it rejects equally the rhetoric by which they were sanctioned and communicated. It elevates the individual and the inward over the social and the outward, and it prefers the unconscious to the self-conscious. The psychologies of Freud and Jung have been seminal in the modern movement in literature. In many respects it is a reaction against REALISM and NATURALISM and the scientific postulates on which they rest. Although by no means can all modern writers be termed philosophical existentialists, EXISTENTIALISM has created a schema within which much of the modern temper can see a reflection of its attitudes and assumptions. The modern revels in a dense and often unordered actuality as opposed to the practical and systematic, and in exploring that actuality as it exists in the mind of the writer it has been richly experimental. What has been distinctively worthwhile in the literature of this century has come, in considerable part, from this modern temper.
"Modernism." A Handbook to Literature, 7th edition. Edited by William Harmon and C. Hugh Holman, Prentice Hall, 1996. 325-36.

The term modernism is widely used to identify new and distinctive features in the subjects, forms, concepts, and styles of literature and the other arts in the early decades of the twentieth century, but especially after World War I (1914-18). The specific features signified by "modernism" vary with the user, but many critics agree that it involves a deliberate and radical break with some of the traditional bases not only of Western art, but of Western culture in general. Important intellectual precursors of modernism, in this sense, are thinkers who had questioned the certainties that had supported traditional modes of social organization, religion, and morality, and also traditional ways of conceiving the human self—thinkers such as Friedrich Nietzsche, Karl Marx, Sigmund Freud, and James G. Frazer, whose 12-volume The Golden Bough (1890–1915) stressed the correspondence between central Christian tenets and pagan, often barbaric, myths and rituals.
Literary historians locate the beginning of the modernist revolt as far back as the 1890s, but most agree that what is called high modernism, marked by an unexampled scope and rapidity of change, came after the first World War. The year 1922 alone was signalized by the simultaneous appearance of such monuments of modernist innovation as James Joyce's Ulysses, T. S. Eliot's The Waste Land, and Virginia Woolf's Jacob's Room, as well as many other experimental works of literature. The catastrophe of the war had shaken faith in the moral basis, coherence, and durability of Western civilization and raised doubts about the adequacy of traditional literary modes to represent the harsh and dissonant realities of the postwar world. T. S. Eliot wrote in a review of Joyce's Ulysses in 1923 that the inherited mode of ordering a literary work, which assumed a relatively coherent and stable social order, could not accord with "the immense panorama of futility and anarchy which is contemporary history." Like Joyce, and like Ezra Pound in his Cantos, Eliot experimented with new forms and a new style that would render contemporary disorder, often contrasting it to a lost order and integration that, he claimed, had been based on the religion and myths of the cultural past. In The Waste Land (1922), for example, Eliot replaced the standard syntactic flow of poetic language by fragmented utterances, and substituted for the traditional type of coherent poetic structure a deliberate dislocation of parts, in which very diverse components are related by connections that are left to the reader to discover, or invent. Major works of modernist fiction, following Joyce's Ulysses (1922) and his even more radical Finnegan's Wake (1939), subvert the basic conventions of earlier prose fiction by breaking up the narrative continuity, departing from the standard ways of representing characters, and violating the traditional syntax and coherence of narrative language by the use of stream of consciousness and other innovative modes of narration. . . . Their new forms of literary construction and rendering had obvious parallels in the break away from representational conventions in the artistic movements of expressionism and surrealism, in the modernist paintings and sculpture of Cubism, Futurism, and Abstract Expressionism, and in the violations of standard conventions of melody, harmony, and rhythm by the modernist musical composers Stravinsky, Schoenberg, and their radical followers.
A prominent feature of modernism is the phenomenon called the avant-garde (a French military metaphor: “advance-guard”); that is, a small, selfconscious group of artists and authors who deliberately undertake, in Ezra Pound’s phrase, to “make it new.” By violating the accepted conventions and proprieties, not only of art but of social discourse, they set out to create evernew artistic forms and styles and to introduce hitherto neglected, and sometimes forbidden, subject matter. Frequently, avant-garde artists represent themselves as “alienated” from the established order, against which they assert their own autonomy; a prominent aim is to shock the sensibilities of the conventional reader and to challenge the norms and pieties of the dominant bourgeois culture. See Renato Poggioli, The Theory of the Avant-Garde (1968). Peter Bürger’s Theory of the Avant-Garde (1984) is a neo-Marxist analysis both of modernism and of its distinctive cultural formation, the avant-garde.
Abrams, M.H., and Geoffrey Galt Harpham, "Modernism." A Glossary of Literary Terms, 9th edition, Wadsworth Cengage Learning, 2009.

Modernist Constellations Of Meaning
- Stylistic innovations - disruption of traditional syntax and form.
- Artist's self-consciousness about questions of form and structure.
- Obsession with primitive material and attitudes.
- International perspective on cultural matters.
- The artist is generally less appreciated but more sensitive, even more heroic, than the average person.
- The artist challenges tradition and reinvigorates it.
- A breaking away from patterned responses and predictable forms.
- Democratic and elitist.
- Traditional and anti-tradition.
- National jingoism and provinciality versus the celebration of international culture.
- Puritanical and repressive elements versus freer expression in sexual and political matters.
- Dramatization of the plight of women.
- Creation of a literature of the urban experience.
- Continuation of the pastoral or rural spirit.
- Continuation of regionalism and local color.
- Fragmentation of traditional literary and artistic styles.
- Collectivism versus the authority of the individual.
- The impact of WWI and the 1918 Bolshevik Revolution in Russia.
- The Jazz Age.
- The disassociated, anomic self.
- The wearing away of traditional class structures.